| |
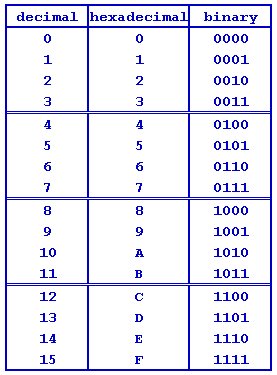
counting - hardware style
- decimal "1" to "10"
- binary "0" to "1111"
- hexadecimal "0" to "F"
|
|
| |
- basics of an operational amplifier.
-
Exercise 5. Build an OpAmp circuit to comply with the specifications below.
-
Power supply : +12 volts, -12 volts, GND (0 volt).
-
Connections according to the circuit above.
-
R(f) + R(i) = 500K. Use a 500K potentiometer to perform the role of a volume control.
-
Generate a "sine wave" using a "Signal Generator" and introduce 50-millivolts between the NInv (connected to GND) and Inv.
-
Connect "Channel A" of the oscilloscope to the Inv input and "Channel B" to the "output" of the OpAmp.
-
Manipulate the "volume control" and watch the behavior of signals shown in channel A and channel B.
|
| |
did you know you could build a digital voltmeter without using computers or microprocessors? you could use only TTL and analog devices using the so-called "successive approximation" method
|
|